Abstract
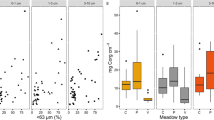
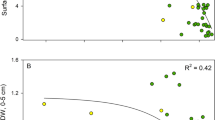
Seagrass meadows are productive ecosystems that contribute to climate change mitigation by accumulating ‘Blue Carbon’ in their plant biomass and sediments. However, there is wide variation in reported sediment carbon stocks (Cstocks) across different global regions and between meadows composed of different seagrass species. Therefore, understanding the drivers for sediment Cstocks variation is crucial to developing effective conservation and restoration projects for seagrass ecosystems. This study analyses the influence of environmental factors on the variation in sediment Cstocks for six intertidal seagrass meadows within the Solent region, in southern England. There were significant differences between sites for all variables, except leaf density, and concentrations of the sediment pore water nutrients. Sediment dry bulk density, mean grain size, sorting coefficient, % mud, elevation above sea level, and pore water salinity showed high levels of association with Cstocks when assessed individually. Multivariate analyses showed that sediment dry bulk density, sorting coefficient, % mud, and pore water pH and concentration of nutrients greatly influenced Cstock. Moreover, sediment characteristics acted in conjunction to explain most of the variation in Cstock among sites. Therefore, sediment characteristics should be considered as important indicators for carbon storage potential in intertidal temperate seagrass meadows.

Maps are adapted from Esri ArcGIS online basemaps, white lines represent roads





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agawin, N. S. R. & C. M. Duarte, 2002. Evidence of direct particle trapping by a tropical seagrass meadow. Estuaries 25: 1205–1209.
Anderson, T. W. & D. A. Darling, 1954. A test of goodness of fit. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 49: 765–769.
Armitage, A. R. & J. W. Fourqurean, 2016. Carbon storage in seagrass soils: long-term nutrient history exceeds the effects of near-term nutrient enrichment. Biogeosciences 13: 313–321.
Benner, R., A. E. Maccubbin & R. E. Hodson, 1984. Anaerobic biodegradation of the lignin and polysaccharide components of lignocellulose and synthetic lignin by sediment microflora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 47: 998–1004.
Björk, M., J. Uku, A. Weil & S. Beer, 1999. Photosynthetic tolerances to desiccation of tropical intertidal seagrasses. Marine Ecology Progress Series 191: 121–126.
Bos, A. R., T. J. Bouma, G. L. J. de Kort & M. M. van Katwijk, 2007. Ecosystem engineering by annual intertidal seagrass beds: sediment accretion and modification. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 74: 344–348.
Brierley, A. S. & M. J. Kingsford, 2009. Impacts of climate change on marine organisms and ecosystems. Current Biology 19: 602–614.
Burdige, D. J., 2007. Preservation of organic matter in marine sediments: controls, mechanisms, and an imbalance in sediment organic carbon budgets? Chemical Reviews 107: 467–485.
Burnside, N., C. Joyce, M. Berg & E. Puurman, 2008. The relationship between micro-topography and vegetation in Estonian coastal wetlands: implications for climate change. Publications Instituti Geographici Universitatis Tartuensis 106: 19–23.
Carrascal, L. M., I. Galva’n & O. Gordo, 2009. Partial least squares regression as an alternative to current regression methods used in ecology. Oikos 118: 681–690.
Carruthers, T. J. B., W. C. Dennison, G. A. Kendrick & M. Waycott, 2007. Seagrasses of south–west Australia: a conceptual synthesis of the world’s most diverse and extensive seagrass meadows. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 21–45.
Chmura, G. L. & G. Hung, 2003. Controls on salt marsh accretion: a test in salt marshes of Eastern Canada. Estuaries 27(1): 70–81.
Cullen-Unsworth, L. C., L. M. Nordlund, J. Paddock, S. Baker, L. J. McKenzie & R. K. F. Unsworth, 2014. Seagrass meadows globally as a coupled social–ecological system: Implications for human wellbeing. Marine Pollution Bulletin 83: 387–397.
D’Souza, E., et al., 2015. Seagrass ecosystems of the Nicobar and Andaman Islands with emphasis on the Dugong dugon status and distribution. PhD Thesis. Faculty of Biology, Madurai Kamaraj University.
Dauwe, B., J. J. Middelburg & P. M. J. Herman, 2001. Effect of oxygen on the degradability of organic matter in subtidal and intertidal sediments of the North Sea area. Marine Ecology Progress Series 215: 13–22.
Dadey, K., T. Janecek & A. Klaus, 1992. Dry bulk density: its use and determination. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program. Scientific Results 26: 551–554.
Dahl, M., D. Deyanova, S. GuÈtschow, M. E. Asplund, L. D. Lyimo, V. Karamfilov, et al., 2016. Sediment properties as important predictors of carbon storage in Zostera marina Meadows: a comparison of four european areas. PLoS ONE 11: e0167493.
De Falco, G., P. Magni, L. M. H. Teräsvuori & G. Matteucci, 2004. Sediment grain size and organic carbon distribution in the Cabras lagoon (Sardinia, Western Mediterranean). Chemistry and Ecology 20: 367–377.
de los Santos, C. B., D. Krause-Jensen, T. Alcoverro, N. Marbà, C. M. Duarte, M. M. van Katwijk, M. Pérez, et al., 2019. Recent trend reversal for declining European Seagrass Meadows. Nature Communications 10: 3356.
de Fouw, J., L. Govers, J. van de Koppel, J. van Belzen, W. Dorigo, M. Sidi Cheikh, M. Christianen, K. van der Reijden, M. van der Geest, T. Piersma, A. Smolders, H. Olff, L. Lamers, J. van Gils & T. van der Heide, 2016. Drought, mutualism breakdown, and landscape-scale degradation of seagrass beds. Current Biology 26: 1051–1056.
Deming, J. W. & J. A. Harass, 1993. The early diagenesis of organic matter: Bacterial activity. In Engel, M. H. & S. A. Macko (eds), Organic Geochemstry: Principles and Application. Springer, Berlin.
Duarte, C. M., 1990. Seagrass nutrients content. Marine Ecology Progress Series 67: 201–207.
Duarte, C. M., 1991. Seagrass depth limits. Aquatic Botany 40: 363–377.
Duarte, C. M., 2002. The future of seagrass meadows. Environmental Conservation 29: 192–206.
Duarte, C. M., 2014. Global change and the future ocean: a grand challenge for marine sciences. Frontiers in Marine Science 1: 1–16.
Duarte, C. M., H. Kennedy, N. Marbà & I. Hendriks, 2011. Assessing the capacity of seagrass meadows for carbon burial: current limitations and future strategies. Ocean and Coastal Management 83: 32–38.
Duarte, C. M., I. J. Losada, I. E. Hendriks, I. Mazarrasa & N. Marba, 2013. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nature Climate Change 3: 961–968.
Dyer, K. R. & H. L. King, 1975. The residual water flow through the Solent, South England. Geophysics Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society. 42: 97–106.
Egea, L. G., R. Jimenez-Ramos, J. J. Vergara, I. Hernandez & F. G. Brun, 2018. Interactive effect of temperature, acidification and ammonium enrichment on the seagrass Cymodocea nodusa. Marine Pollution Bulletin 134: 14–26.
El-Hacen, E. M., T. J. Bouma, G. S. Fivash, A. A. Sall, T. Piersma, H. Olff & L. L. Govers, 2018. Evidence for ‘critical slowing down’ in seagrass: a stress gradient experiment at the southern limit of its range. Scientific Reports 8: 17263.
Enriquez, S., C. M. Duarte & K. Sand-Jensen, 1993. Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: the importance of detritus C:N:P content. Oecologia 94: 457–471.
Enriquez, S., N. Marba, C. M. Duarte, B. I. van Tussenbroek & G. Reyes-Zavala, 2001. Effects of seagrass Thalassia testudinum on sediment redox. Marine Ecology Progress Series 219: 149–158.
Environment Agency, 2016a. Nitrate vulnerable zone (NVZ) designation 2017 – Eutrophic Waters (Estuaries and Coastal Waters) Datasheet—NVZ Name: Portsmouth Harbour, Langstone Harbour and Chichester Harbour—the purposes of the Nitrate Pollution Prevention Regulations 2015. http://apps.environment-agency.gov.uk/static/documents/nvz/NVZ2017_ET7_Newtown_Medina_Eastern_Yar_Datasheet.pdf. Accessed 06 September 2019.
Environment Agency, 2016b. Nitrate vulnerable zone (NVZ) designation 2017—Eutrophic Waters (Estuaries and Coastal Waters) Datasheet—NVZ Name: Newtown Harbour, Medina Estuary, and Eastern Yar (Bembridge Harbour)—the purposes of the Nitrate Pollution Prevention Regulations 2015. http://apps.environment-agency.gov.uk/static/documents/nvz/NVZ2017_ET7_Newtown_Medina_Eastern_Yar_Datasheet.pdf. Accessed 06 September 2019.
Fabricius, K. E., C. Langdon, S. Uthicke, C. Humphrey, S. Noonan, G. De’ath, R. Okazaki, N. Muehllehner, M. S. Glas & J. M. Lough, 2011. Losers and winners in coral reefs acclimatised to elevated carbon dioxide concentrations. Nature Climate Change 1: 165–169.
Folk, R. L. & W. C. Ward, 1957. Brazos river bar: a study of significance of grain size parameters. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 27: 3–26.
Fonseca, M. S. & J. A. Cahalan, 1992. A preliminary evaluation of wave attenuation by four species of seagrass. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 35: 565–576.
Fourqurean, J. W., J. C. Zieman & G. V. N. Powell, 1992. Relationships between porewater nutrients and seagrasses in a subtropical carbonate environment. Marine Biology 114: 57–65.
Fourqurean, J. W., C. M. Duarte, H. Kennedy, N. Marbà, M. Holmer, M. A. Mateo, E. T. Apostolaki, G. A. Kendrick, D. Krause-Jensen, K. J. McGlathery & O. Serrano, 2012a. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nature Geoscience 5: 505–509.
Fourqurean, J. W., G. A. Kendrick, L. S. Collins, R. M. Chambers & M. A. Vanderklift, 2012b. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus storage in subtropical seagrass meadows: examples from Florida Bay and Shark Bay. Marine & Freshwater Research 63: 967–983.
Gacia, E. & C. M. Duarte, 2001. Elucidating sediment retention by seagrasses: sediment deposition and resuspension in a Mediterranean (Posidonia oceanica) meadow. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 52: 505–514.
Gacia, E., C. M. Duarte & J. J. Middelburg, 2002. Carbon and nutrient deposition in the Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica). Limnology and Oceanography 47: 23–32.
Garrard, S. L. & N. J. Beaumont, 2014. The effect of ocean acidification on carbon storage and sequestration in seagrass beds; a global and UK context. Marine Pollution Bulletin 86: 138–146.
Gray, S. J. & M. Elliott, 2009. Ecology of Marine Sediments: From Science to Management. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Gullström, M., L. D. Lyimo, M. Dahl, G. S. Samuelsson, M. Eggertsen, E. Anderberg, et al., 2018. Blue carbon storage in tropical seagrass meadows relates to carbonate stock dynamics, plant-sediment processes and landscape context: insights from the Western Indian Ocean. Ecosystems 21: 551–566.
Hall-Spencer, J. M., R. Rodolfo-Metalpa, S. Martin, E. Ransome, M. Fine, S. M. Turner, S. J. Rowley, D. Tedesco & M.-C. Buia, 2008. Volcanic carbon dioxide vents show ecosystem effects of ocean acidification. Nature 454: 96–99.
Harding, S., L. Nelson & T. Glover, 2016. Solent Oyster Restoration Project Management Plan. Blue Marine Foundation (BLUE), London: 49.
Head, K. H., 1986. Manual of Soil Laboratory Testing, Vol. 3. Wiley, New York.
Hedges, J. I. & R. G. Keil, 1995. Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis. Marine Chemistry 49: 81–115.
Heiri, O., A. F. Lotter & G. Lemcke, 2001. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology 25: 101–110.
Hemminga, M. A. & C. M. Duarte, 2000. Seagrass Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hendriks, I. E., T. Sintes, T. J. Bouma & C. M. Duarte, 2008. Experimental assessment and modelling evaluation of the effects of seagrass (P. oceanica) on flow and particle trapping. Marine Ecology Progress Series 356: 163–173.
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. & J. F. Bruno, 2010. The impact of climate change on the world’s marine ecosystems. Science 328: 1523–1528.
Howard, J., S. Hoyt, K. Isensee, E. Pidgeon, & M. Telszewski (eds), 2014. Coastal Blue Carbon: Methods for assessing carbon stocks and emissions factors in mangroves, tidal salt marshes, and seagrass meadows. Arlington: Conservation International, Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Howard, J. L., A. Perez, C. C. Lopes & J. W. Fourqurean, 2016. Fertilization changes seagrass community structure but not Blue Carbon storage: results from a 30-year field experiment. Estuaries and Coasts. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0085-1.
Howard, J., A. Sutton-Grier, D. Herr, J. Kleypas, E. Landis & E. Mcleod, 2017. Clarifying the role of coastal and marine systems in climate mitigation. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 15: 42–50.
Invers, O., J. Romero & M. Perez, 1997. Effects of pH on seagrass photosynthesis, a laboratory and field assessment. Aquatic Botany 59: 185–194.
Jackson, M. L., 1967. Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi: 498p.
Jones, B. L. & R. K. F. Unsworth, 2016. The perilous state of seagrass in the British Isles. Royal Society Open Science 3: 150596.
Jordà, G., N. Marbà & C. M. Duarte, 2012. Mediterranean seagrass vulnerable to regional climate warming. Nature Climate Change 2: 812–824.
Keil, R. & J. Hedges, 1993. Sorption of organic matter to mineral surfaces and the preservation of organic matter in coastal marine sediments. Chemical Geology 107: 385–388.
Kennedy, H. & M. Björk, 2009. Seagrasses. In Laffoley, D. & G. Grimsditch (eds), The management of natural coastal carbon sinks in coastal ecosystems: investigating and realizing the potential. IUCN, Gland: 23–30.
King, D., 2010. Solent Waders and Brent Goose Strategy 2010. Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trust.
Koch, E. W., J. D. Ackerman, J. Verduin & M. van Keulen, 2006. Fluid dynamics in seagrass ecology: from molecules to ecosystems. In Larkum, A. W. D., R. J. Orth & C. M. Duarte (eds), Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Dordrecht: 193–225.
Lavery, P. S., M. Á. Mateo, O. Serrano & M. Rozaimi, 2013. Variability in the carbon storage of seagrass habitats and its implications for global estimates of Blue Carbon ecosystem service. PLoS ONE 8: e73748.
Longstaff, B., N. Loneragan, W. O’donohue & W. Dennison, 1999. Effects of light deprivation on the survival and recovery of the seagrass Halophila ovalis (R. Br.) Hook. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 234: 1–27.
Lovelock, C. E., T. Atwood, J. Baldock, C. M. Duarte, S. Hickey, P. S. Lavery, P. Masque, P. I. Macreadie, A. M. Ricart, O. Serrano & A. Steven, 2017. Assessing the risk of carbon dioxide emissions from blue carbon ecosystems. Frontiers in Marine Science 15: 257–265.
Macreadie, P. I., K. Allen, B. P. Kelaher, P. J. Ralph & C. G. Skilbeck, 2012. Paleoreconstruction of estuarine sediments reveal human-induced weakening of coastal carbon sinks. Global Change Biology 18: 891–901.
Macreadie, P. I., M. E. Baird, S. M. Trevathan-Tackett, A. W. D. Larkum & P. J. Ralph, 2013. Quantifying and modelling the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrass meadows: a critical assessment. Marine Pollution Bulletin 83: 430–439.
Malvern Instruments Ltd, 2007. Mastersizer 2000 User Manual (MANO384, issue 1.0). https://www.malvernpanalytical.com/en/products/technology/light-scattering/laser-diffraction. Accessed 21 August 2017.
Marbà, N., D. Krause-Jensen, T. Alcoverro, S. Birk, A. Pedersen, J. M. Neto, S. Orfanidis, J. M. Garmendia, I. Muxika, A. Borja, K. Dencheva & C. M. Duarte, 2013. Diversity of European seagrass indicators: patterns within and across regions. Hydrobiologia 704: 265–278.
Marbà, N., E. Diaz-Almela & C. M. Duarte, 2014. Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) loss between 1842 and 2009. Biological Conservation 176: 183–190.
Marbà, N., Krause‐Jensen, D., Masqué, P., & Duarte, C. M. 2018. Expanding greenland seagrass meadows contribute new sediment carbon sinks. Scientific Reports https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32249-w
Marin-Guirao, L., A. M. Atucha, J. L. Barba, E. M. Lopez & A. J. G. Fernandez, 2005. Effects of mining wastes on a seagrass ecosystem: metal accumulation and bioavailability, seagrass dynamics and associated community structure. Marine Environmental Research 60: 317–337.
Marsden, A. L. & J. C. Chesworth, 2015. Inventory of eelgrass beds in Hampshire and the Isle of Wight 2015, Section One: Report. Version 7: May 2015. Hampshire.
Martínez-Crego, B., A. Vergés, T. Alcoverro & J. Romero, 2008. Selection of multiple seagrass indicators for environmental biomonitoring. Marine Ecology Progress Series 361: 93–109.
Martínez-Crego, B., I. Olivé & R. Santos, 2014. CO2 and nutrient-driven changes across multiple levels of organization in Zostera noltii ecosystems. Biogeosciences 11: 7237–7249. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-7237-2014.
Mateo, M. A., J. Cebrián, K. Dunton & T. Mutchler, 2006. Carbon flux in seagrass ecosystems. In Larkum, A., R. J. Orth & C. M. Duarte (eds), Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Dordrecht: 159–192.
Maxwell, P. S., J. S. Ekl, M. M. Katwijk & K. R. O. Van Brien, 2017. The fundamental role of ecological feedback mechanisms for the adaptive management of seagrass ecosystems: a review. Biological Review. 92: 1521–1538.
Mayer, L. M., 1994. Relationship between mineral surfaces and organic carbon concentrations in soils and sediments. Chemical Geology 114: 347–363.
Mazarrasa, I., N. Marbà, J. Garcia-Orellana, P. Masqué, A. Arias-Ortiz & C. M. Duarte, 2017a. Effect of environmental factors (wave exposure and depth) and anthropogenic pressure in the C sink capacity of Posidonia oceanica meadows. Limnology and Oceanography 62: 1436–1450.
Mazarrasa, I., N. Marbà, J. Garcia-Orellana, P. Masqué, A. Arias-Ortiz & C. M. Duarte, 2017b. Dynamics of carbon sources supporting burial in seagrass sediments under increasing anthropogenic pressure. Limnology and Oceanography 62: 1451–1465.
Mazarrasa, I., J. Samper-Villarreal, O. Serrano, P. S. Lavery, C. E. Lovelock, N. Marba & C. M. Duarte, 2018. Habitat characteristics provide insights of carbon storage in seagrass meadows. Marine Pollution Bulletin 134: 106–117.
McGlathery, K. J., P. Berg & R. Marino, 2001. Using porewater profiles to assess nutrient availability in seagrass-vegetated carbonate sediments. Biogeochemistry 56: 239–263.
McLeod, C. R., M. Yeo, A. E. Brown, A. J. Burn, J. J. Hopkins & S. F. Way (eds), 2005. The Habitats Directive: selection of Special Areas of Conservation in the UK, 2nd edn, Joint.
McLeod, E., G. Chmura, S. Bouillon, R. Salm, M. Bjork, C. Duarte, C. Lovelock, W. Schlesinger & B. Silliman, 2011. A blueprint for blue carbon: toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7: 362–370.
Michalski, R. & I. Kurzyca, 2006. Determination of nitrogen species (nitrate, nitrite and ammonia ions) in environmental samples by ion chromatography (review). Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 15: 5–18.
Miyajima, T., M. Hori, M. Hamaguchi, H. Shimabukuro, H. Adachi & H. Yamano, 2015. Geographic variability in organic carbon stock and accumulation rate in sediments of East and Southeast Asian seagrass meadows. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 29: 397–415.
Montefalcone, M., 2009. Ecosystem health assessment using the Mediterranean sea-grass Posidonia oceanica: a review. Ecological Indicators 9: 595–604.
Murray, B. C., L. Pendleton & S. Sifleet, 2011. State of the science on coastal blue carbon: a summary for policy makers. In Nicholas Institute for Environmental Policy Solutions Report NIR 11-06, P. 1-4 3.
Nelleman, C., E. Corcoran, C. M. Duarte, L. Valdés, C. De Young, L. Fonseca & G. Grimsditch, 2009. Blue Carbon. A Rapid Response Assessment. United Nations Environment Programme, GRID-Arendal. Birkeland Trykkeri AS, Norway.
Oreska, M. P. J., K. J. McGlathery & J. H. Porter, 2017. Seagrass Blue Carbon spatial patterns at the meadow-scale. PLoS ONE 12: e0176630.
Orth, R. J., T. J. B. Carruthers, W. C. Dennison, C. M. Duarte, J. W. Fourqurean & K. L. Heck, 2006. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56: 987–996.
Palacios, S. L. & R. C. Zimmerman, 2007. Response of eelgrass Zostera marina to CO2 enrichment: possible impacts of climate change and potential for remediation of coastal habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 344: 1–13.
Pedersen, M. Ø., O. Serrano, M. A. Mateo & M. Holmer, 2011. Decomposition of Posidonia oceanica matte in a climate change setting. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 65: 169–182.
Pedrosa-Pàmies, R., A. Sanchez-Vidal, A. Calafat, M. Canals & R. Durán, 2013. Impact of storm-induced remobilization on grain size distribution and organic carbon content in sediments from the Blanes Canyon area, NW Mediterranean Sea. Progress in Oceanography 118: 122–136.
Pendleton, L., D. C. Donato, B. C. Murray, S. Crooks, W. A. Jenkins, S. Sifleet, C. Craft, J. W. Fourqurean, J. B. Kauffman, N. Marba, P. Megonigal, E. Pidgeon, D. Herr, D. Gordon & A. Baldera, 2012. Estimating global “blue carbon” emissions from conversion and degradation of vegetated coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 7: e43542.
Peralta, G., L. A. Van Duren, E. P. Morris & T. J. Bouma, 2008. Consequences of shoot density and stiffness for ecosystem engineering by benthic macrophytes in flow dominated areas: a hydrodynamic flume study. Marine Ecology Progress Series 368: 103–115.
Perry, C. J. & W. C. Dennison, 1999. Microbial nutrient cycling in seagrass sediments. AGSO Journal of Australian Geology and Geophysics 17: 227–231.
Ralph, P. J., 1999. Photosynthetic response of Halophila ovalis (R. Br.) Hook. f. to combined environmental stress. Aquatic Botany 65: 83–96.
Ralph, P. J., D. Tomasko, K. Moore, S. Seddon & C. M. O. Macinnis-Ng, 2006. Human impacts on seagrasses: eutrophication, sedimentation and contamination. In Larkum, A. W. D., R. J. Orth & C. M. Duarte (eds), Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Dordrecht: 567–593.
Repolho, T., B. Duarte, G. Dionísio, J. R. Paula, A. R. Lopes, I. C. Rosa, et al., 2017. Seagrass ecophysiological performance under ocean warming and acidification. Scientific Reports 7: 41443.
Ricart, A. M., M. Pérez & J. Romero, 2017. Landscape configuration modulates carbon storage in seagrass sediments. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 185: 69–76.
Roca, G., T. Alcoverro, D. Krause-Jensen, T. J. S. Balsby, M. Katwijk, N. van Marbà, et al., 2016. Response of seagrass indicators to shifts in environmental stressors: a global review and management synthesis. Ecological Indicators 63: 310–323.
Röhr, M. E., M. Holmer, J. K. Baum, M. Björk, D. Chin, L. Chalifour, et al., 2018. Blue carbon storage capacity of temperate eelgrass (Zostera marina) meadows. Global Biogeochemical Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GB005941.
Rozaimi, M., O. Serrano & P. S. Lavery, 2013. Comparison of carbon stores by two morphologically different seagrasses. Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia 96: 81–83.
Russell, B. D., S. D. Connell, S. Uthicke, N. Muehllehner, K. E. Fabricius & J. M. Hall-Spencer, 2013. Future seagrass beds: can increased productivity lead to increased carbon storage? Marine Pollution Bulletin 73: 463–469.
Samper-Villarreal, J., C. E. Lovelock, M. I. Saunders, C. Roelfsema & P. J. Mumby, 2016. Organic carbon in seagrass sediments is influenced by seagrass canopy complexity, turbidity, wave height, and water depth. Limnology and Oceanography 61: 938–952.
Samper-Villarreal, J., P. J. Mumby, M. I. Saunders, C. Roelfsema & C. E. Lovelock, 2018. Seagrass organic carbon stocks show minimal variation over short time scales in a heterogenous subtropical seascape. Estuaries and Coasts 41: 1732–1743.
Saunders, M. I., J. Leon, S. R. Phinn, D. P. Callaghan, K. R. O’Brien, C. M. Roelfsema, C. E. Lovelock, M. B. Lyons & P. J. Mumby, 2013. Coastal retreat and improved water quality mitigate losses of seagrass from sea level rise. Global Change Biol. 19: 2569–2583.
SeaView Report-Chichester Harbour, 2017. Environment Agency and Sussex Inshore Fisheries and Conservation Authority. http://arunwesternstreams.org.uk/sites/default/files/uploads/Sussex%20SeaView%20report%20Final.pdf. Accessed 10 April 2019.
Serrano, O., P. S. Lavery, M. Rozaimi & M. A. Mateo, 2014. Influence of water depth on the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrass. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 28: 950–961.
Serrano, O., A. M. Ricart, P. S. Lavery, M. A. Mateo, A. Arias-Ortiz, P. Masque, A. Steven & C. M. Duarte, 2016. Key biogeochemical factors affecting soil carbon storage in Posidonia meadows. Biogeosciences 13: 4581–4594.
Short, F. T. & H. A. Neckles, 1999. The effects of global climate change on seagrasses. Aquatic Botany 63: 169–196.
Short, F. T. & S. Willie-Echeverria, 1996. Natural and human-induced disturbance of seagrasses. Environmental Conservation 23: 17–27.
Sunda, W. G. & W.-J. Cai, 2012. Eutrophication induced CO2-acidification of subsurface coastal waters: interactive effects of temperature, salinity, and atmospheric PCO2. Environmental Science and Technology 46: 10651–10659.
ter Braak, C. J. F., 1986. Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67: 1167–1179.
U.S. EPA., 2007. Method 9056A, Determination of Inorganic Anions by Ion Chromatography. U.S. EPA, Cincinnati.
Valle, M., G. Chust, A. del Campo, M. S. Wisz, S. M. Olsen, J. M. Garmendia & A. Borja, 2014. Projecting future distribution of the seagrass Zostera noltii under global warming and sea level rise. Biological Conservation 170: 74–85.
van Keulen, M. & M. A. Borowitzka, 2003. Seasonal variability in sediment distribution along an exposure gradient in a seagrass meadow in Shoalwater Bay, Western Australia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 57: 587–592.
Verduin, J. J. & J. O. Backhaus, 2000. Dynamics of plant–flow interactions for the seagrass Amphibolis antarctica: field observations and model simulations. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 50: 185–204.
Ward, R. D., P. A. Teasdale, N. G. Burnside, C. B. Joyce & K. Sepp, 2014. Recent rates of sedimentation on irregularly flooded Boreal Baltic coastal wetlands: responses to recent changes in sea level. Geomorphology 217: 61–72.
Ward, R. D., N. G. Burnside, C. B. Joyce & K. Sepp, 2016. Importance of microtopography in determining plant community distribution in Baltic Coastal Wetlands. Journal of Coastal Research 321: 1062–1070.
Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck Jr., A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short & S. L. Williams, 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 12377–12381.
Wilson, A. M., M. Huettel & S. Klein, 2008. Grain size and depositional environment as predictors of permeability in coastal marine sands. Estuarine, Coast and Shelf Science. 80: 193–199.
Wentworth, C. K., 1922. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. The Journal of Geology 30: 377–392.
Wood, J. C., 2015. Determination of moisture content and total organic carbon within basin environments: loss-on-ignition. Geomorphological Techniques 1(2): 3.
Ye, Y., N. F. Y. Tam, Y. S. Wong & C. Y. Lu, 2003. Growth and physiological responses of two mangrove species (Bruguiera gymnorrhiza and Kandelia candel) to waterlogging. Environmental and Experimental Botany 49: 209–221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guest editors: Koen Martens, Sidinei M. Thomaz, Diego Fontaneto & Luigi Naselli-Flores / Emerging Trends in Aquatic Ecology III
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, M.A.C., Ward, R.D. & Joyce, C.B. Environmental drivers of sediment carbon storage in temperate seagrass meadows. Hydrobiologia 847, 1773–1792 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04153-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04153-5